
Work Smarter, Live Better with Ergonomics
Did you know poor ergonomics causes 60% of musculoskeletal disorders, lowers productivity by 25%, and increases absenteeism by 30%?
Understanding Ergonomics: Your Workers Are Your Assets
Ergonomics is the scientific study focused on optimizing work environments to align with employees’ physical capabilities. By improving workspaces, tools, and processes, ergonomics reduces strain, prevents injuries, and enhances comfort. This supports employee health, boosts productivity, and increases job satisfaction. We offer advanced injury prevention ergonomic solutions, driving innovation in musculoskeletal care for a safer, more efficient workplace.
The goal of ergonomics is to make work processes safer, more efficient, and less physically demanding, reducing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) and accidents. By focusing on human-centered design, ergonomics enhances productivity while safeguarding workers’ health.

Key Benefits of Ergonomics in the Workplace
Applying ergonomics principles brings several advantages to both workers and industries, such as:





The Role of Human Factors in Ergonomics
Ergonomics is grounded in human factors, which refers to understanding how the human body interacts with its physical environment. By considering human body dimensions (known as anthropometry), ergonomic designs ensure that tools, machinery, and workspaces are optimized to fit the physical needs of users.
For example, tasks requiring repetitive physical effort can lead to fatigue or injury if the design doesn’t account for the body’s limitations. By applying ergonomic principles, such as adjusting the height of workstations or providing proper seating, the physical demands on workers are minimized, promoting long-term health and efficiency.
Types of Ergonomics
Physical Ergonomics
Focuses on designing workspaces that match human anatomical, physiological, and biomechanical characteristics. It aims to improve the work experience by aligning jobs with people’s capabilities, reducing work-related musculoskeletal disorders.
Cognitive Ergonomics
Focuses on mental processes like perception, memory, reasoning, and motor response, and how they influence interactions between humans and system elements.
Organizational Ergonomics
Focuses on optimizing sociotechnical systems, including structures, policies, and processes. It aims to improve teamwork, job satisfaction, and schedules, enhancing communication and boosting productivity.
Physical Ergonomics
Focuses on designing workspaces that match human anatomical, physiological, and biomechanical characteristics. It aims to improve the work experience by aligning jobs with people’s capabilities, reducing work-related musculoskeletal disorders.

Workplace Environment
Workplace ergonomics focuses on creating an environment that promotes employee health, safety, and productivity. Key elements include:
Lighting: Adequate lighting reduces eye strain and boosts focus, keeping employees alert throughout the day.
Noise Levels: Minimizing excessive noise to prevent hearing loss.
Temperature Control: Maintaining a comfortable temperature to ensure employees can focus without discomfort.
Equipment Placement: Organizing furniture and tools efficiently to limit unnecessary movements.
Cognitive Ergonomics
Focuses on mental processes like perception, memory, reasoning, and motor response, and how they influence interactions between humans and system elements.



Organizational Ergonomics
Focuses on optimizing sociotechnical systems, including structures, policies, and processes. It aims to improve teamwork, job satisfaction, and schedules, enhancing communication and boosting productivity.
Innovative Ergonomics
Cognitive ergonomics pertains to mental processes such as perception, memory, reasoning, and motor response. Important aspects include:
Mental Workload: Ensuring employees aren’t overwhelmed by excessive cognitive demands.
Decision-Making: Streamlining processes and task structures to facilitate quick, accurate decision-making.
Information Processing: Clearly organizing information so employees can easily access and understand it.
By optimizing cognitive tasks, this approach enhances employee performance, reduces errors, and helps maintain focus over extended periods.

Our Prem Ergo Approaches to
Ergonomic Design
Biomechanical Approach
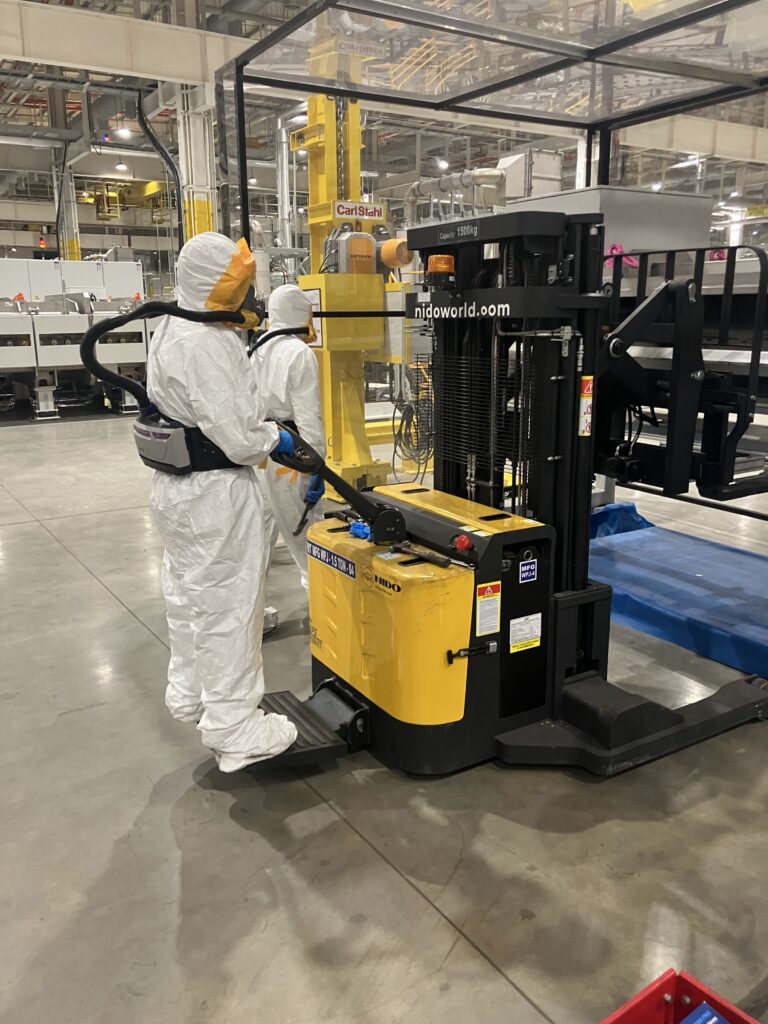
The biomechanical approach connects the principles of physics to the human body, assessing mechanical stresses during work. Key areas of focus include:
Body Movements: Ensuring proper mechanics during lifting, reaching, and bending to prevent physical strain.
Force Exertion: Identifying tasks that involve excessive force, like heavy lifting, and recommending safer techniques.
Postural Stress: Reducing prolonged periods in uncomfortable or unnatural postures that can strain muscles and joints.
This approach seeks to minimize physical stress on the body, preventing injuries and enhancing overall worker comfort and efficiency.


Epidemiological Approach
The epidemiological approach investigates groups of people to analyze data and uncover the root causes of workplace injuries and health issues. Key elements include:
Injury Patterns: Tracking and analyzing workplace injuries, particularly repetitive strain injuries, to identify patterns and prevent future incidents.
Health Impact: Examining how long-term exposure to poor ergonomic conditions leads to chronic issues, such as back pain or carpal tunnel syndrome.
Risk Factors: Identifying environmental, organizational, or physical factors that contribute to employee health problems.
By analyzing data and trends, companies can make informed decisions to prevent injuries and improve workplace health.
The Prem Ergo Methodology:
A Personalized Approach to Ergonomics
We conduct an in-depth and critical observation of work processes and operator activities at various workstations. This approach allows us to identify potential ergonomic challenges and opportunities for improvement.
Observation
Photography and videography
Workstation analysis
Human product interface
Other physiological measurements
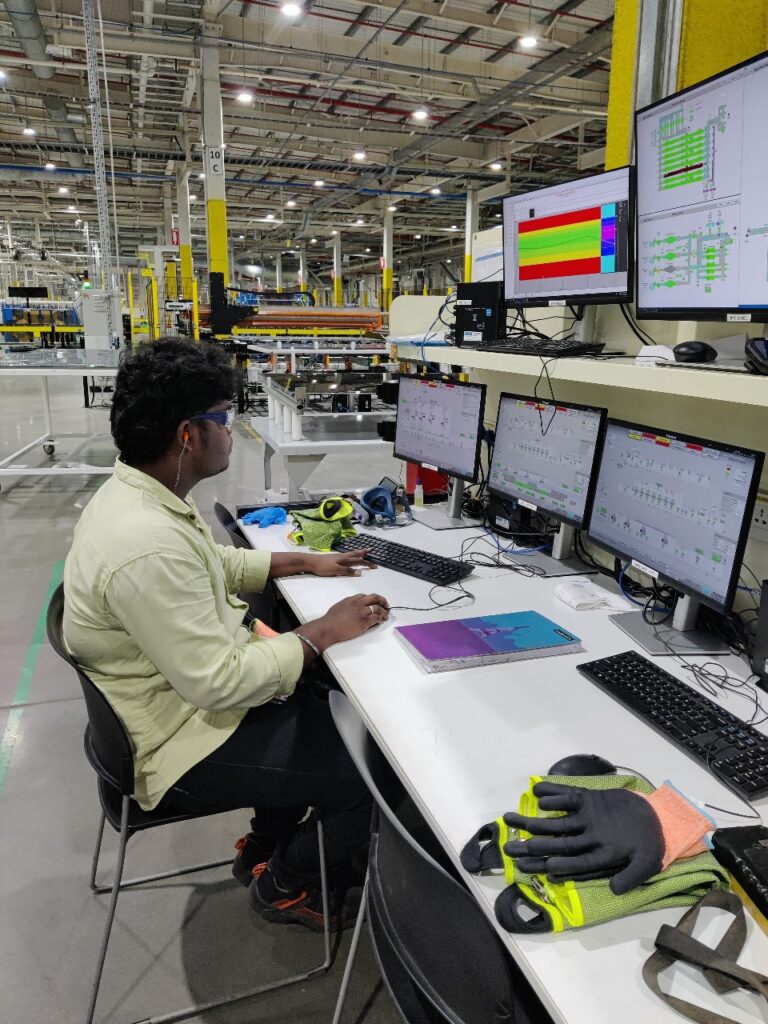

AI-Powered Tools for Ergonomic Evaluation and MSD Risk Assessment
Prem Ergo leverages advanced AI technology to provide real-time assessments of Musculoskeletal Disorder (MSD) risks in the workplace. By delivering data-driven insights, we assist organizations in identifying ergonomic hazards, minimizing injuries, and enhancing productivity while reducing operational costs. With a strong emphasis on AI-powered solutions, Prem Ergo enables organizations to create safer, healthier work environments and nurture a culture of well-being and efficiency.
